Prompt discovery, in the context of large language models and prompt engineering, refers to the systematic process of identifying, optimizing, and fine-tuning prompts that elicit desired responses from the language model. It involves a blend of linguistic, computational, and experimental techniques to formulate prompts that yield accurate and contextually relevant outputs from the model.
The goal of prompt discovery is to uncover the most effective prompts and combinations thereof to achieve specific tasks, while also considering factors like response quality, model performance, and computational efficiency.
In highly technical terms, prompt discovery encompasses several complex problems and activities:
-
Prompt Formulation: This involves crafting prompts that are clear, unambiguous, and tailored to the desired task. Different phrasings and structures might lead to variations in model behavior, so prompt engineers need to experiment with syntax and semantics to achieve optimal results.
-
Prompt Permutations: Researchers need to explore various permutations of prompts by altering wording, adding context, or using different query types. Systematically generating and testing different prompt variations is a crucial part of prompt discovery to identify which specific formulations generate the desired outputs.
-
Fine-tuning Parameters: Discovering the ideal fine-tuning parameters for each prompt and model combination is a complex optimization problem. Researchers must experiment with factors like learning rates, batch sizes, and optimization algorithms to fine-tune the model for specific prompts.
-
Benchmarking and Comparison: Comparing response quality across different prompt permutations, models, and settings is essential. This involves devising appropriate evaluation metrics to quantitatively assess the performance of the model in response to different prompts and making informed decisions based on these metrics.
-
Generalization and Transfer Learning: Investigating the extent to which prompts can be generalized across tasks or domains is a challenging problem. Researchers need to explore how prompts can be adapted or transferred to different tasks without sacrificing performance.
-
Exploration of Novel Prompts: As the field evolves, prompt engineers must continuously come up with innovative prompt formulations that push the boundaries of the model's capabilities. This might involve experimenting with new query structures, linguistic constructs, or contextual cues.
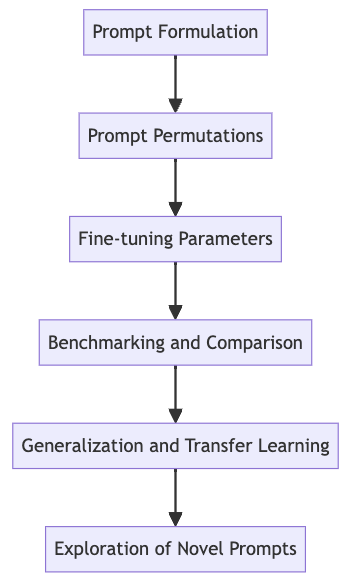
Figure 1: Flowchart illustrating the steps in prompt discovery. Starting with prompt formulation, it progresses through prompt permutations, fine-tuning parameters, benchmarking and comparison, generalization and transfer learning, to the exploration of novel prompts.
For prompt discovery, a range of tools, both existing and potentially developed in the future, can be instrumental:
-
Automated Prompt Generation: AI-assisted tools that automatically generate prompt variations based on input specifications could expedite the discovery process.
-
Prompt Optimization Algorithms: Advanced optimization algorithms tailored for prompt discovery, including genetic algorithms or reinforcement learning approaches, could efficiently explore the prompt space.
-
Interactive Prompt Testing Environments: User-friendly interfaces that allow prompt engineers to interactively test and fine-tune prompts with real-time model feedback can facilitate rapid iteration.
-
Prompt Benchmarking Platforms: Comprehensive platforms for benchmarking prompt performance across various tasks, models, and settings could aid in making informed prompt selection decisions.
-
Semantic Analysis Tools: Tools that provide detailed semantic analysis of prompt-response pairs can help identify patterns and nuances in model behavior, guiding prompt formulation.
-
Natural Language Understanding Frameworks: Advanced NLU frameworks that provide insights into model comprehension and reasoning processes can inform prompt design for better results.
-
Transfer Learning Techniques: Techniques that enable efficient transfer of knowledge from one prompt to another could support prompt generalization across tasks.
-
Continuous Model Monitoring: Real-time monitoring tools that track model performance in response to different prompts can aid in prompt discovery over time.
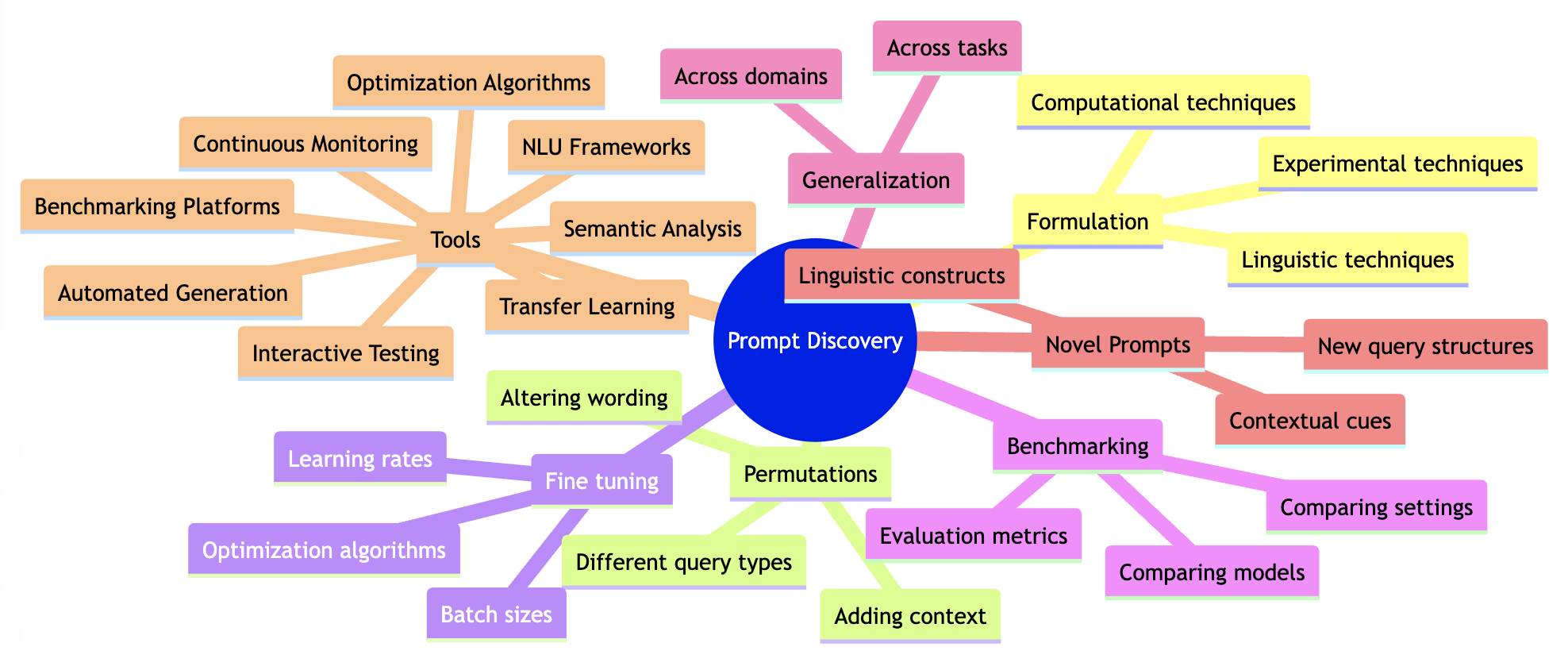
*Figure 2: Mindmap illustrating the key aspects of prompt discovery. It includes formulation, permutations, fine-tuning, benchmarking, generalization, novel prompts, and the different tools involved in the process.
